The world of cryptocurrencies, digital assets, blockchain, and more specifically, Bitcoin has introduced a new dynamic to the work of online day trading and investing. For experienced traders and investors in financial markets, they have been able to transfer their knowledge of how markets behave and capitalize on their experience in a new environment.
However, the novelty of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies attracted the attention of people from all different backgrounds. Whether it be people with software engineering backgrounds, technology enthusiasts, privacy advocates, and forward-looking individuals, many of them struggle to grasp the concept of trading and investing in Bitcoin.
What many new Bitcoin investors and traders overlook is that there is a dramatic difference between the underlying technology and ecosystem which powers Bitcoin and the marketplace which drives the price through supply and demand. Although it is important, unfortunately knowing how blockchain ledgers function, how to mine various cryptocurrencies, or how wallets work is not relevant to becoming a successful Bitcoin investor.
In this complete guide to investing and trading Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, we will begin with the very basics of how to trade and invest. The guide will start by describing what money is; then it will cover how financial markets work and then move into different factors that influence the price of Bitcoin at any given time. If you stick with us until the end of this guide, we shall cover the differences between trading and investing and ultimately describe different types of Bitcoin investment strategies.
An introduction to money and monetary policy
According to economists, money is a verifiable record that is widely accepted as a medium of exchange, a unit of account, and a store of value. There are additional qualities that are expected of money too, which are to be portable, durable, divisible, and fungible, which essentially contribute towards ensuring the primary functions are fulfilled.
In our minds, we anchor units of money to the cost of various products and services that we pay for. Most of us know how much a can of Coca-Cola (or Pepsi) costs in our domestic currency. If you have a one-euro coin, you know that you can take that coin all over Europe and use it to buy a can of Coke in any supermarket.
Let’s analyze that coin and compare it against the definition of money.
The euro is issued by the Central Bank of Europe, which makes it verifiable. The coin is small enough to fit in your pocket and is minted using a robust alloy, which makes it portable and durable. A one-euro coin has a fixed value engraved on it and is no different from any other one-euro coins in circulation, which makes it a unit of account and fungible. If you visit any store within the Euro-Zone, it can be used in exchange for products, which makes it widely accepted and a medium of exchange. If the item you purchase costs less than a euro, the seller can give change in lower denominations, which makes it divisible.
If, in twenty years from today, you conduct that same exercise, would you still be able to buy a can of Coke with a one-euro coin? It is unlikely that you would be able to, which means that the euro is not a store of value, and there does not fall under the definition of money.
If the euro is not money, what is it? It’s a fiat-based currency.
Fiat-based currency is quite simply, what you probably thought money was. The euro, U.S. dollar, Japanese yen, and Swiss franc are all examples of currencies.
What are cryptocurrencies?
The inherent flaw of a fiat currency system is that they depend on trust. For example:
- You trust the government not to devalue it through inflation.
- You must trust your bank to safeguard your currency and not accidentally or deliberately lose it.
- You trust that other people in your day to day life will also consider your currency as valuable.
Cryptocurrencies are designed in such a way that trust is no longer a requirement for a monetary system to function.
The term cryptocurrency is a mesh of the terms cryptography and currency. The cryptographic properties possessed by cryptocurrencies are what makes them spectacular.
There are many thousands of different cryptocurrencies in circulation, and more broadly, digital assets and tokens. All of these various mutations of cryptocurrencies possess slightly different features; however, they all share a few fundamental characteristics.
The prevailing feature of a cryptocurrency is that spending and verifying ownership can only be proven cryptographically. To prove ownership and be able to transfer balances from one address to another, a corresponding private key is required. A transaction must be verified using a proof-of-work system, where verifiers, also known as miners, validate the authenticity of a transaction. Once a transaction is processed, it is archived in the databases, known as the blockchain, which is replicated in many different locations, which makes it incredibly difficult to alter all instances. Without a private key, it is impossible to transfer balances due to the level of high-level encryption.
Cryptocurrencies can have a wide-ranging list of attributes. However, defining what a cryptocurrency is can turn into somewhat of a philosophical debate.
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency to launch and be widely adopted. Prior to Bitcoin, there were similar attempts. A lot of the characteristics of Bitcoin were inherited from previous concepts and later cryptocurrencies, evolved from Bitcoin.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was the first of its kind cryptocurrency and to this day remains the most widely used and popularised cryptocurrency. The origin of Bitcoin is unclear, and its history is fascinating. Bitcoin has had a profound influence on the world and opened many people’s minds to a new breed of monetary policy.
Unlike national currencies such as the euro, Bitcoin is entirely detached from any central government. Instead, Bitcoin is governed by technology and powered by numerous individuals and independent organizations.
Without getting too technical, and staying on the path of describing Bitcoin from a financial, investment, and trading perspective, here is a summary of how Bitcoin can be characterized as a currency.
| Bitcoin transactions are processed and recorded on a publicly visible ledger, known as the blockchain. Pending transactions are grouped into blocks, and every ten minutes a block will be processed by a network of competing independent organizations, known as miners. The miner credited with completing the block of the transaction will collect the sum of transaction fees pledged by sender initiators and be paid a fixed reward for processing a block of transactions. The reward miners earn for processing blocks of transactions is currently set at 6.25 BTC per block; this reward is halved every 210,000 blocks. The total supply of Bitcoins that can be created is 21 million. The maximum precision of a Bitcoin is nine-decimals, which means the smallest transaction that can be made is 0.000000001 BTC. |
Besides Bitcoin, there are hundreds of other cryptocurrencies, and tokens used for transferring value in different ecosystems and niches around the world.
Investing and Trading Bitcoin
So far, in this guide, we have focused on what Bitcoin is as a financial instrument and the characteristics it holds as a currency. Knowing what Bitcoin is from an economic perspective, helps us to understand the fundamental value it has as an asset.
Going further into this guide, we shall explore key investment concepts, how Bitcoin has been integrated with traditional finance, how you can buy and sell Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, and most important of all, how to know when to buy and sell.
What are financial markets?
The definition of a financial market is incredibly broad and essentially describes any financial asset (or instrument) that can be traded within an open marketplace. The two primary ways that financial instruments are traded is in a decentralized over-the-counter (OTC) transaction or in an exchange venue where multiple buyers and sellers can participate and place their orders.
Some well-known examples of financial markets are:
- Stocks traded on exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or the NASDAQ.
- Government and corporate bonds traded either on exchanges or between a broker and private buyers and sellers in what’s known as an over-the-counter market.
- Commodities such as gold, oil, and agricultural products traded on exchanges like the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT).
- Currencies traded on the decentralized foreign exchange market between numerous brokers, dealers, and private institutions as well as many independent exchange venues.
- Various types of derivatives, such as futures, options, and CFDs, used for placing short term transactions which do not require settlement at the conclusion of the contract.
The most recent asset class to join the list of financial markets are cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies can be traded on many independent crypto exchanges, they can be purchased from and sold to brokers, and they can be traded as derivatives. The most common types of derivatives used for trading Bitcoin are futures contracts and contract-for-difference (CFDs).
What is the difference between trading and investing?
Trading and investing are concepts that define a style and objective for buying and selling financial instruments. The verbs trading and investing are often used interchangeably. The confusion arises from the principle that to invest, you need to trade, and to trade, you need to invest. However, each phrase relates to a specific style of investing.
How to invest in cryptocurrencies
Investing is essentially buying an asset and holding it for long periods, often for years or decades, expecting long-term price appreciation. Investing is a very hands-off and passive style of profiting from the financial markets. Purchasing property, starting a business, buying stocks or gold bullion are typically defined as investments.
In the crypto community, someone who is a HODL-er would be considered an investor. If you incrementally buy a few hundred euros of Bitcoin or crypto each month, with no intention of selling it or spending it in the near future, that would make you an investor.
Here is an example of what it would look like if an investor had been buying Bitcoin between Monday the 2nd of March 2020 and Friday the 27th of November 2020 and purchased 500 dollars worth of BTC near the end or the start of each month when they may receive their salary.
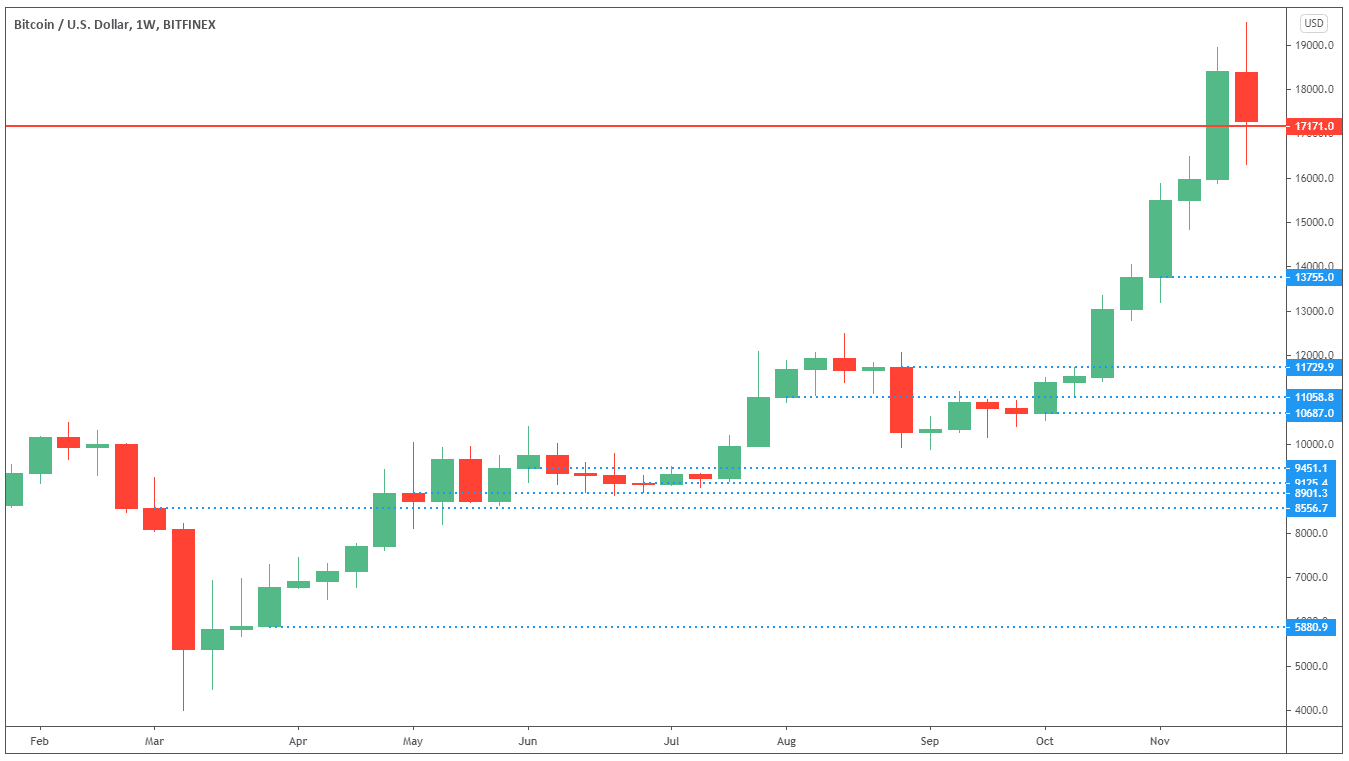
| Purchase Date | BTC/USD Price | Amount of BTC |
| 02.03.20 | 8556.7 | 0.058433742 |
| 30.03.20 | 5880.9 | 0.085021 |
| 04.05.20 | 8901.3 | 0.05617157 |
| 01.06.20 | 9451.1 | 0.052903895 |
| 29.06.20 | 9125.4 | 0.054792119 |
| 03.08.20 | 11058.8 | 0.045212862 |
| 31.08.20 | 11729.9 | 0.042626109 |
| 05.10.20 | 10687.0 | 0.046785815 |
| 02.11.20 | 13755.0 | 0.036350418 |
| 27.11.20 | 17171.0 | 0.029118863 |
After nine months of investing, the investor would have accumulated just over half a Bitcoin (0.507416393 BTC) for a total investment of $5,000.
If we consider that the current price of Bitcoin as of the 27th of November 2020 is $17,171 and you hold $8,712.85 worth of BTC, which you paid $5,000 for; that makes the investor a profit of $3712.85 and is a return on investment of 74.26%.
An investor would be unlikely to exit their investment in Bitcoin after nine months, and would probably continue following this routine over many more months, and even years.
What is interesting about this strategy is the investor did not consider the price at which each new Bitcoin was purchased and simply bought at the opening price of the week. Some investors will strategically wait for prices to fall to certain levels, known as resistance levels, to buy at a slightly cheaper price.
How to trade cryptocurrencies
Trading is essentially the activity of frequently buying and selling different financial instruments to gain profit from small price increments over a day, week or month. Trading is a more proactive approach to profiting from the financial markets. Traders try to identify undervalued or overvalued instruments and identify possible trend changes.
By trading instead of investing, a trader can use their capital multiple times instead of allocating it to a single investment held for long periods. There are different styles of trading, such as scalping, day-trading, and position-trading. By using a short-term trading strategy, traders are capable of earning more than investors who simply buy and hold investments. However, there is much more work involved in actively trading and far more room for mistakes to occur.
Here is an example of six short term Bitcoin trades, all placed within twenty-four hours of each other. In this example, the trader is purchasing $5,000 of BTC with each trade.
As you will notice from the diagram below, the trader buys BTC at moments when the market dips and sells when the price peaks before pivoting and retreating to a lower price where the trader can buy again at a lower price.
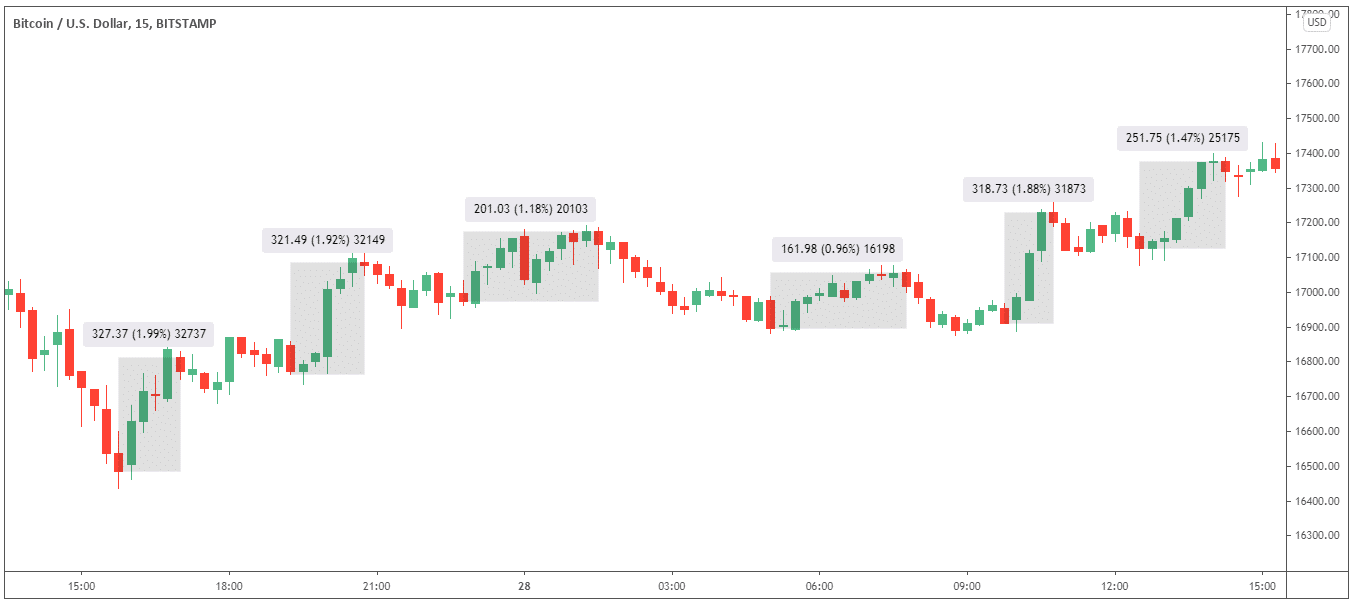
You might be wondering how this trader can predict when the price will go up and down. Traders use different forms of analysis to predict how prices will move over a day and try to profit from those fluctuations.
There are signs that traders can interpret to highlight that an uptrend is losing momentum and may begin retracting. Once the price has fallen to a certain level, it may show signs that momentum is slowing and the market may pivot and start a new uptrend.
| Open Price | Close Price | Trade Size | Profit | Trade Duration |
| 16486.03 | 16772.32 | 0.30329 ($5,000) | $99.34 | 1h 15m |
| 16763.36 | 17077.53 | 0.29827 ($5,000) | $95.90 | 1h 30m |
| 16973.13 | 17138.86 | 0.29459 ($5,000) | $59.34 | 2h 45m |
| 16895.75 | 17018.25 | 0.29594 ($5,000) | $48.06 | 2h 45m |
| 16911.33 | 17207.28 | 0.29566 ($5,000) | $94.24 | 1h |
| 17125.21 | 17346.53 | 0.29197 ($5,000) | $73.55 | 1h 45m |
The table above shows a summary of these six trades. In total, the trader made a profit of $470.43, which is a return on investment of 9.41% in less than twenty-four hours. The shortest trade held was just an hour, and the longest was 2-hours & 45-minutes.
Crypto trading vs investing
In the examples given above, it might seem that trading cryptocurrencies are more profitable than investing. However, it’s not quite as straightforward as that. In the Bitcoin trading example given, there was no consideration for losing trades, or fees and spreads the investor would pay to an exchange for filling orders, which can eat into profitability. Moreover, when you’re actively trading, your mind is constantly thinking about the market, and whether you’re making money, losing money or missing opportunities. Some traders find this very uncomfortable.
To be successful at trading and investing, you don’t just need to understand how markets function and prices move. You also need to understand all of the psychological factors at play. Many traders are responsible for their own demise because of their self-doubt and constantly second-guessing themselves.
What influences the value of an asset?
In a financial market, the price of an asset naturally adjusts to fit supply and demand. Although financial markets can be mysterious and complex, as a general rule, when these two factors are displaced, the price of an asset will go up or down.
If demand increases, but supply does not, prices will rise. The price increases because there is more competition buying the asset but not enough sellers to fulfill the demand. Conversely, when demand decreases, but supply does not, prices will fall. The price decreases because there is more competition selling the asset, but not enough buyers to take the supply.
Even if there is no change in demand, but the supply decreases, that can also trigger an increase in price as there are still not enough sellers to satisfy the amount of demand, and vice versa.
How supply and demand affect the price of Bitcoin
Bitcoin and other cryptos are incredibly susceptible to the influence of supply and demand and shifts in the equilibrium of buyers and sellers. In the past, and recently, we’ve seen the price of Bitcoin rise and fall dramatically. The rapid increase in the price of Bitcoin occurs when more people want to buy BTC than those who wish to sell it. What causes the price of BTC to fall rapidly is when there are too many sellers.
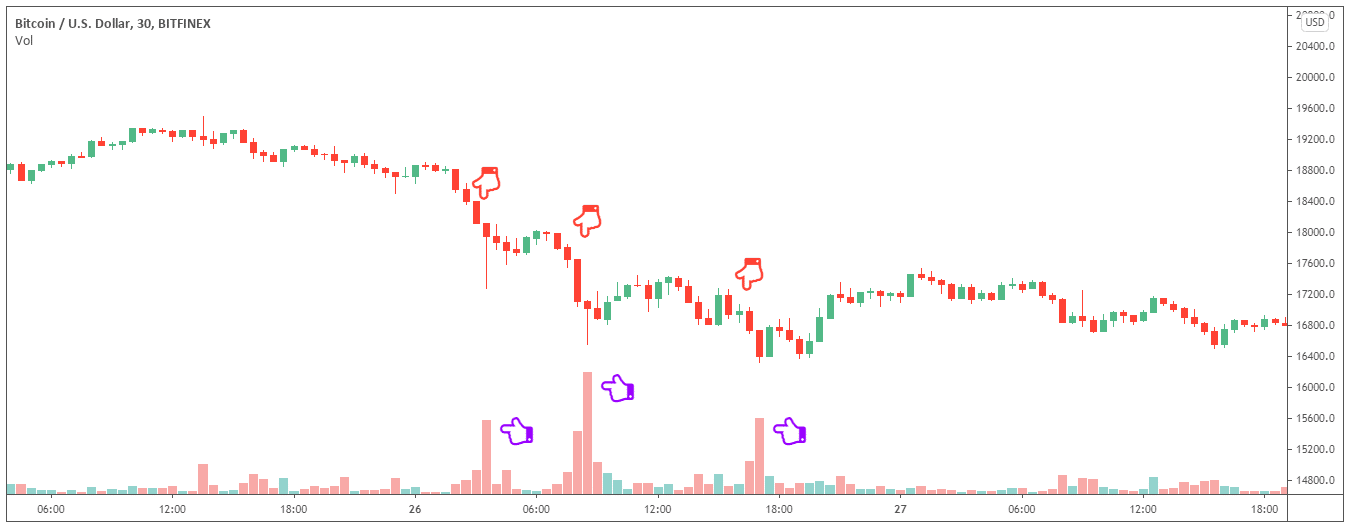
For example, look at the chart above. It shows the price of BTC falling from $18,800 to $16,100 over the period of 15-hours. Below the candlesticks, there is a volume indicator, which reflects the number of sell orders. The purple pointers highlight significant increases in selling pressure, which ultimately triggers a sell-off.
Bitcoin is incredibly susceptible to the influence of supply and demand. The amount of BTC being traded on open spot exchanges is actually very limited in comparison not just to other financial markets, but to the total supply of BTC.
If we consider recent data, as of the 27th of November 2020, the 30-day average market cap of BTC in USD is $291.4bn, whereas the peak trading volume on major spot exchanges in recent months was just $867.6m; these figures suggest that far less 1% of circulating BTC is really being traded on exchanges.

Types of cryptocurrency market analysis
To be successful at trading or investing, you need to time your trades and plan precisely when to buy and sell. For day-traders, these skills are essential, but they are also vital for investors to help buy their investments at more advantageous prices to increase long-term profitability ultimately.
There are a variety of techniques used to predict the behavior of financial markets, and they can be broadly categorized as technical analysis, price analysis, fundamental, and sentiment analysis.
Technical analysis
When you log in to any cryptocurrency exchange trading platform, the very first thing that you’ll notice in the center of the screen is a price chart that shows you how the price has moved over a given period. Most crypto trading applications come loaded with dozens of technical analysis tools pre-installed. For example, the popular TradingView charting application offers more than 100 technical analysis indicators.
Don’t be alarmed. You don’t need to learn how hundreds of technical analysis indicators work to become a successful crypto trader. Most traders try to pinpoint a handful of tools that offer the highest amount of accuracy.
Traders use technical analysis indicators to understand how the price of a cryptocurrency behaved previously and attempt to predict how it might move in the future. Some techniques have proven to be highly effective at gauging where and when to buy and sell cryptocurrencies.
There are four categories of indicators; trend, oscillators, volatility and volume.
Moving averages play a vital role in technical analysis of the cryptocurrency markets. A moving average can smooth out the price volatility that is shown on a typical candlestick chart and helps you to clearly see if there is a trend or not. Besides this, the moving average acts as a foundation of many other trading indicators.
Bollinger Bands are a popular volatility indicator that helps traders to time their trades. The Bollinger Bands indicator is composed of three bands. The middle band is a simple moving average. The upper and lower bands are slightly modified simple moving averages.
The theory behind a Bollinger Bands trading system starts with the principle that the price will always return to the middle band, the moving average. A buy signal is generated when the price breaks the lower band, and a sell signal is generated when the price breaks the middle or upper band, depending on the strategy.
In the example below, we can see a few examples of the BTC price, breaking the lower band and promptly returning and breaking the middle band.
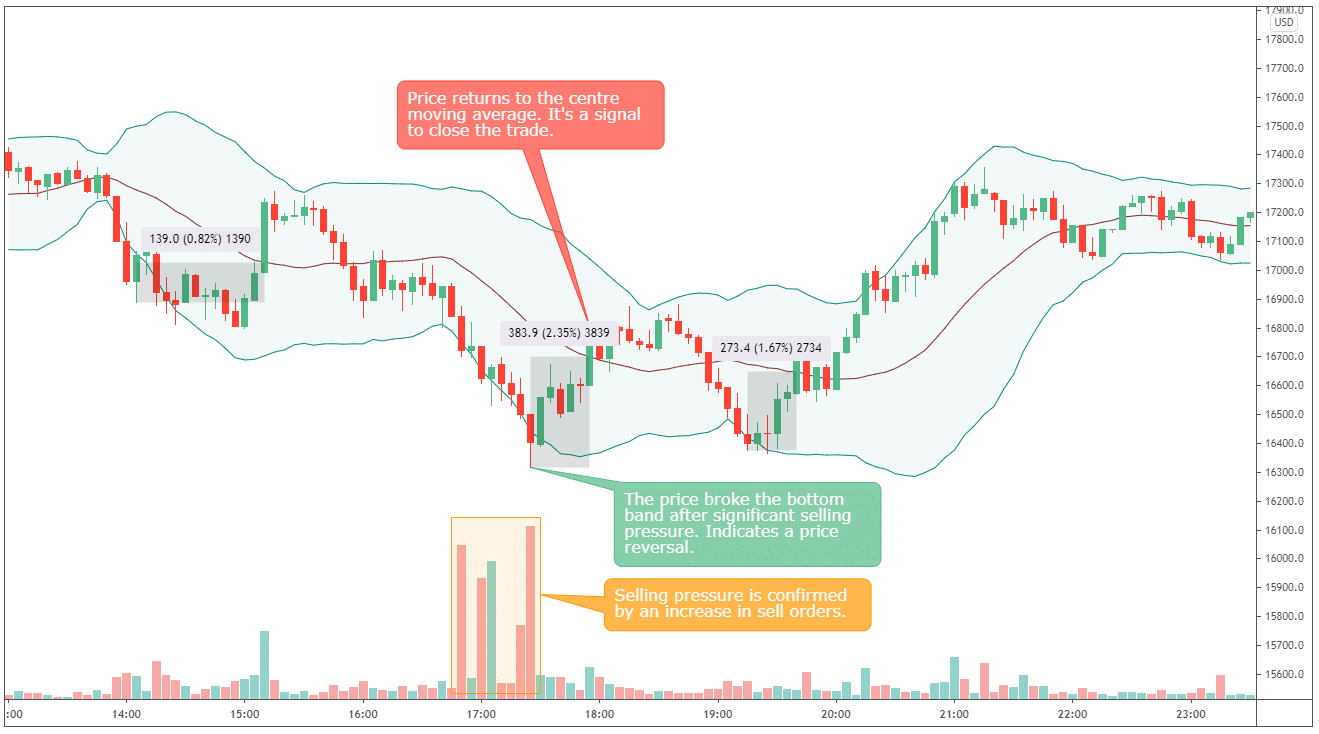
If those three trades had been played out, under the same conditions as in the previous example, the three trades would have grossed a profit of $242.48.
| Open Price | Close Price | Trade Size | Profit | Trade Duration |
| 16890 | 17029 | 0.29604 ($5,000) | $41.27 | 1h 5m |
| 16317 | 16700.9 | 0.30643 ($5,000) | $117.66 | 30m |
| 16376 | 16649.4 | 0.30533 ($5,000) | $83.56 | 25m |
Fundamental analysis
Most investors and traders rely on fundamental analysis to understand what factors could influence the supply and demand of an asset and therefore, its price. As mentioned earlier, the Bitcoin and cryptocurrency market is highly susceptible to shifts in supply and demand as sentiment within the crypto-community shifts.
In the crypto market, a single piece of news can send shockwaves throughout the market, triggering a rally or a dump.
News like PayPal supporting Bitcoin payments is a positive sign for the adoption of Bitcoin; the news was credited for the subsequent BTC price rally. Other news like a high-profit hack can be interpreted as a negative sign for the adoption of Bitcoin; this news would be expected to cause a negative sentiment in the market.
Although many alt-coins move in correlation with BTC, meaning a win for Bitcoin, is a win for most cryptos, there is a lot of fundamental information that affects individual cryptos and tokens. For example, if there is some favorable news about the crypto exchange Binance, it’s likely the BNB coin issued by Binance will appreciate.
TIP!
| The CryptoCaptain Bull Market Compass has been developed with long-term Bitcoin and cryptocurrency investors in mind. The Bull Market Compass automatically and continuously analyses market sentiment in online media and derives investment decisions from it. Equipped with this powerful tool, investors can know when to buy and when to wait, as they invest in the cryptocurrency market. |
Discover Bull Market Compass
Where to buy and trade cryptocurrencies
As of 2020, there are numerous avenues for buying, selling, and exchanging cryptocurrencies. It wasn’t like that several years ago.
One of the legacy platforms for buying Bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies is Coinbase, which makes it incredibly easy for residents of most countries to buy crypto using their bank card or by making a wire transfer.
There are many different options available and choosing the right company to cooperate with entirely depends on your investment or trading objectives. The two main types of crypto exchanges are fiat-to-crypto and crypto-to-crypto.
Fiat-to-crypto exchanges allow you to buy and sell cryptocurrencies that are quoted against fiat currencies, such as dollars, euros, and pounds. Besides exchanging fiat into crypto and vice versa, they should also offer reliable and affordable on-ramps and off-ramps; which is how you initially find your account to buy crypto and how to withdraw if you ultimately decide to sell.
Crypto-to-crypto exchanges don’t allow you to fund an account using fiat, which means you need to own crypto already to fund the exchange account. A crypto-to-crypto exchange will offer trading pairs such as Ethereum versus Bitcoin (ETH/BTC) or Ripple versus Bitcoin (XRP/BTC). Many crypto-to-crypto exchanges offer stablecoins, which are a specific type of cryptocurrency which is pegged to the value of a fiat currency. Stablecoins are very helpful when trading, as many opportunities occur when cryptocurrencies appreciate against the U.S. dollar.
Most fiat-to-crypto exchanges have a limited number of cryptocurrencies available to invest in or trade. The reason is that banking partners will be very hesitant when cooperating with crypto exchanges is because some coins possess strong privacy characteristics. Banks and card processing companies will be uneasy about cooperating with exchanges that offer cryptocurrencies which appear to pose a threat to anti-money laundering initiatives. Therefore, you will notice crypto-to-fiat exchanges offering fewer options to trade on their exchange.
Conclusion: are you ready to enter the cryptocurrency market?
One of the hardest parts of trading or investing in cryptocurrencies and digital assets is knowing when to buy and when not to buy. If you’re new to trading and investing, then the best thing you can do at this stage is to continue to read detailed guides much like this one. There is plenty to learn by reading and following the comprehensive articles we publish on the CryptoCaptain blog. Besides being armed with the right information and know-how, you need to equip yourself with the right tools to help analyze the markets and make actionable predictions that ultimately make money.

